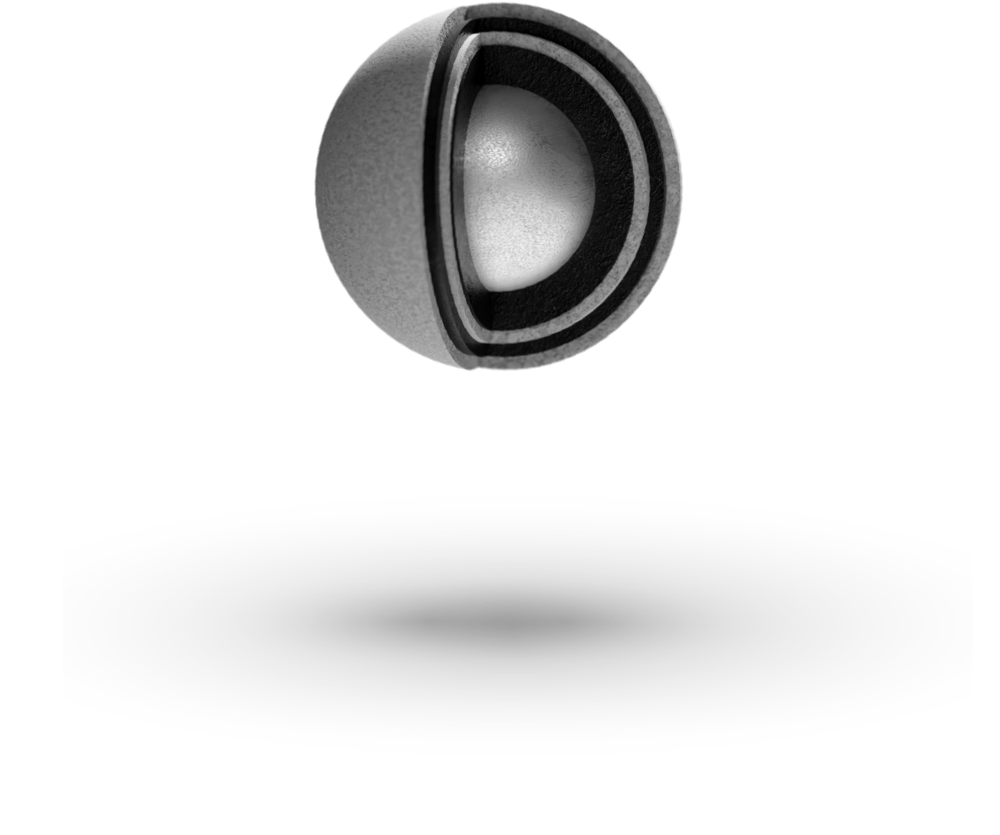
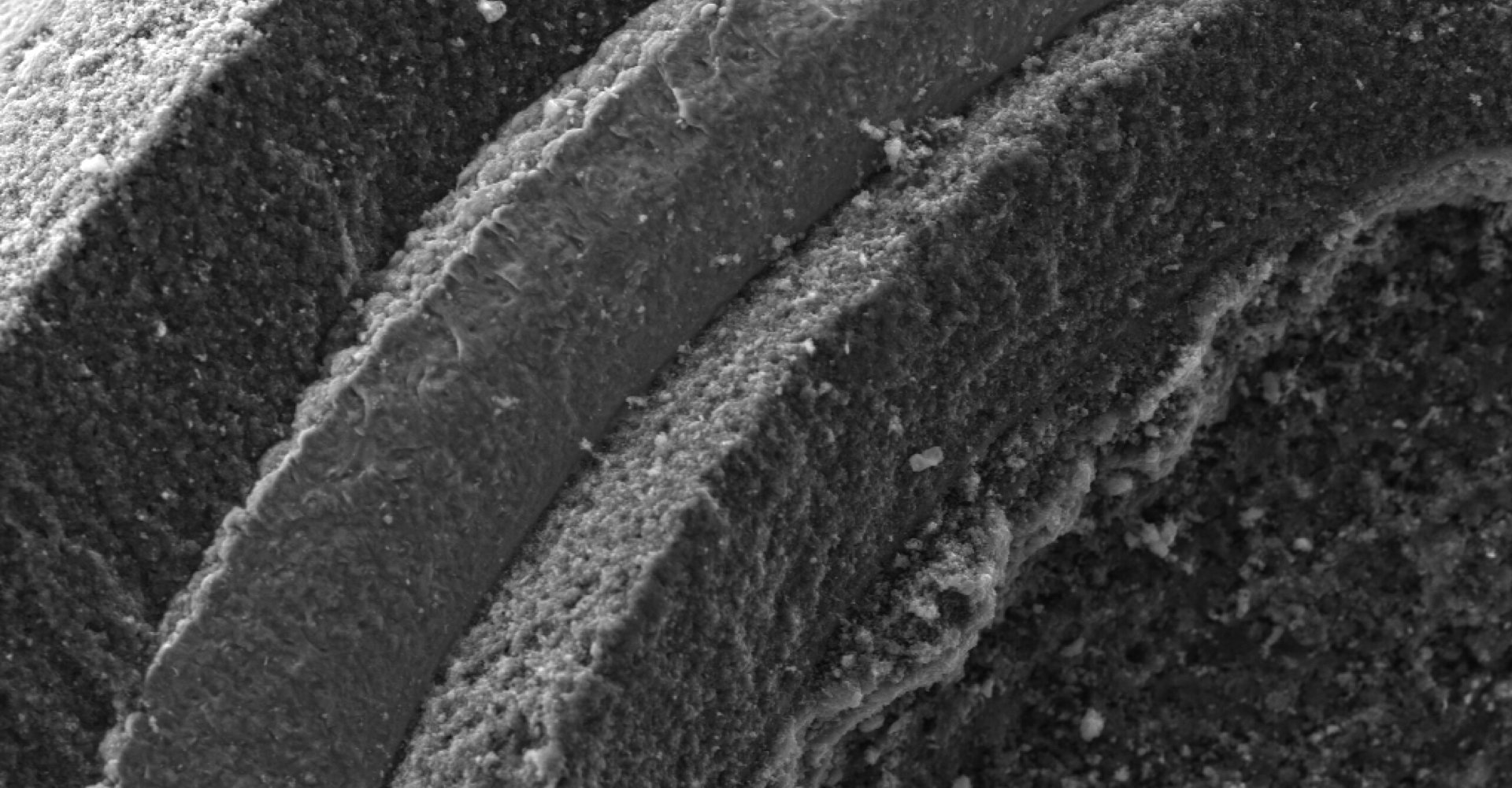
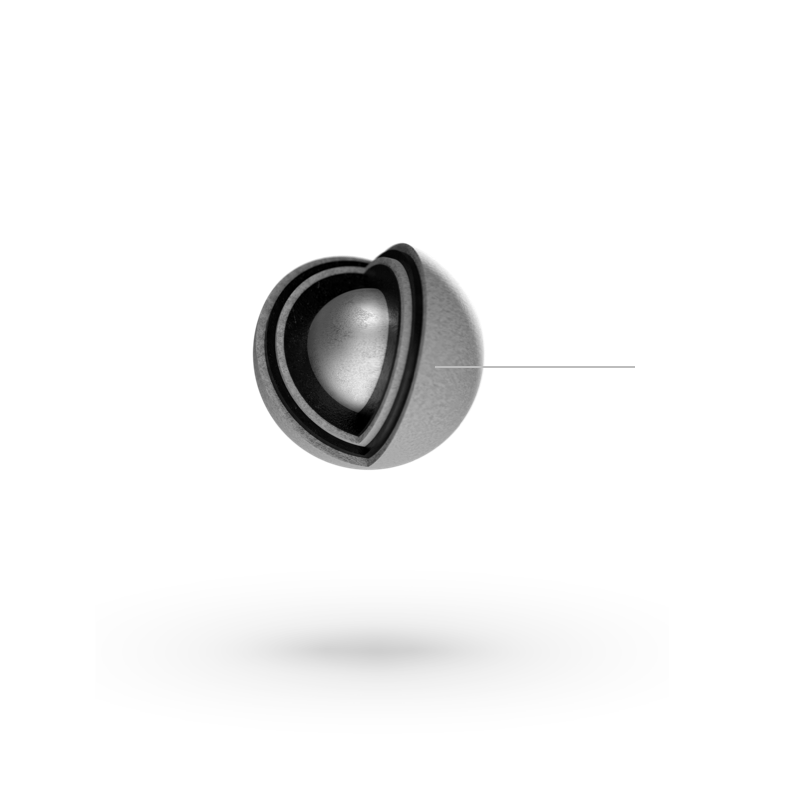
Particle Layers
Coated particle layers are applied to uranium bearing particles using a fluidized-bed chemical vapor deposition (FB-CVD) process.
Carbon Buffer Layer
The first layer which consists of approximately 50% dense pyrocarbon and serves two primary functions. The buffer layer provides void space to accommodate fission gases released from the kernel and kernel swelling due to solid fission products. The buffer layer also provides distance between the kernel and the other coating layers to prevent concentrated damage in those layers from high-energy fission product recoils.
Pyrolytic Carbon (PyC) Layer
The PyC layer is highly dense so that it functions as an effective barrier to gasses and diffusion of many of the actinides and fission products. The IPyC layer is responsible for contributing to retention of fission gasses during irradiation and protecting the kernel from HCl vapor, which is a byproduct of the silicon carbide (SiC) layer deposition process. The OPyC layer also contributes to the retention of fission products and acts as a substrate to bond the graphite matrix.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
The SiC layer critically serves as both the primary source of structural strength for the particle and the primary barrier to the release of fission products which are not retained within the kernel.
Zirconium Carbide (ZrC)
To improve the high-temperature performance of TRISO fuel, ZrC is often substituted for the SiC is coated particle fuel. The ZrC layer provides fission product retention at higher temperatures and in extreme reducing environments. This refractory ceramic is often preferred Nuclear Thermal Propulsion applications.
“We’ve reinvented the most robust & safe nuclear fuel on earth”
We’re Hiring
Developing state-of-the-art, high technology solutions for reactors and fuel requires both traditional nuclear and non-traditional engineering skills and experience. We’re looking for capabilities in solution development, multi-disciplinary analysis, systems engineering, facility design, test planning, logistics, management, and system integration.